Introduction: The Significance of Għar Dalam Cave Malta
Għar Dalam Cave Malta is one of the most important prehistoric sites in the Mediterranean. This cave, located in the southern part of Malta, preserves layers of fossils and human artifacts that reveal the island’s distant past. Archaeologists consider the cave a vital record of Ice Age migrations, ancient animal life, and early human presence. Visitors and researchers alike are captivated by the mysteries preserved within its walls, from extinct elephants and hippos to debated Neanderthal remains.
Layers of Għar Dalam Cave Reveal Malta’s Past
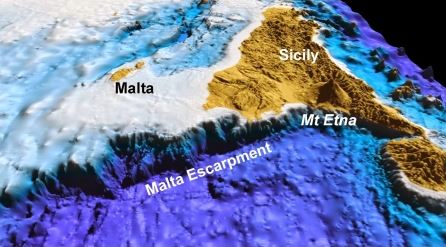
Għar Dalam Cave Malta contains stratified layers, each offering a glimpse into different periods of the island’s history. The lowest layers hold fossilized remains of Pleistocene animals, such as hippopotami, elephants, deer, and bears. These animals likely migrated to Malta when sea levels dropped during glacial periods, forming a temporary land bridge connecting Malta to Sicily and mainland Europe. Over time, floods and river movements carried remains into the cave, creating a unique archaeological record.
Ice Age Migrations and Fossil Discoveries
The cave provides evidence of repeated migrations during the Ice Ages. As the North Polar Ice Cap advanced and retreated, animals sought new pastures, traveling south through the land bridge that connected Malta to Sicily. Fossils found in Għar Dalam Cave Malta indicate that multiple species, including extinct elephants and hippopotami, settled on the island at different times. The sedimentary layers show how environmental changes shaped the migration patterns and survival of these animals.
Human Presence and Neanderthal Debate
Among the most debated finds in Għar Dalam Cave Malta are two human molars discovered in 1917. Archaeologist Giuseppe Despott noted their fused roots, a trait associated with Neanderthal man. This suggested that Neanderthals might have reached Malta during the Pleistocene. Later studies debated the molars’ context, questioning whether they arrived naturally via flooding or represent genuine habitation. Modern researchers, including Dr. Charles Savona Ventura, argue that their placement alongside large mammal remains strengthens the case for early human presence.
The Cultural and Scientific Importance
Għar Dalam Cave Malta is more than just a fossil repository. It offers insights into early migration patterns, human adaptation, and environmental changes over tens of thousands of years. The cave’s stratified layers also provide a timeline of Malta’s natural history, showing the co-existence of humans and extinct animals. For archaeologists, paleoanthropologists, and historians, the site remains a key location for understanding prehistoric life in the Mediterranean.
Visiting Għar Dalam Cave Malta Today
Today, Għar Dalam Cave Malta is open to the public as a museum and research site. Visitors can walk through the preserved layers, see fossilized remains, and learn about the Ice Age animals and early humans who once inhabited the island. The cave’s exhibits emphasize the connection between geology, climate changes, and human history, making it a unique educational and cultural experience.
Internal Link Suggestions:
-
Cave Malta Mysteries https://ancient360.eu/ghar-dalam-cave-malta-mystery/
Outbound Link Suggestions:
-
Homo Sapiens in Europe https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06923-7
-
Megalithic Temples of Malta https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/132/